SASE Overlay: An Intro

You may have heard of Secure Access Service Edge, or SASE – but CoIP Access Platform uses a SASE overlay. What is a SASE overlay, and makes the CoIP SASE Overlay different?
Covered in this article:
- What is the CoIP SASE Overlay?
- How does the CoIP SASE Overlay work?
- What are the benefits of the SASE overlay approach?
- What problems does a SASE overlay solve?

What is the CoIP SASE Overlay?
The CoIP SASE Overlay is a cybersecurity mesh that connects and protects users, endpoints, applications, and devices across distributed environments, without having to connect the environments together.
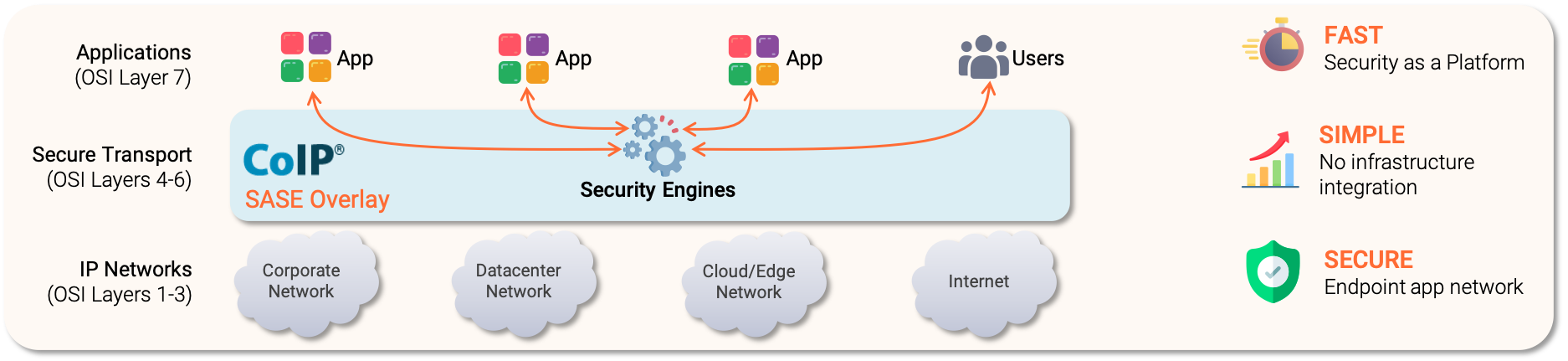
The CoIP SASE Overlay
The legacy approach to dealing with hybrid and remote applications is to connect networks together, so that applications using the network can reach each other. The goal of this approach is to expand the network – remote sites and clouds are assigned chunks of the corporate IP address space, connecting to the corporate network hub with VPNs. In other words, infrastructure build is the legacy answer to hybrid and remote. As users and applications become increasingly dynamic, the infrastructure build model becomes difficult to scale – not to mention that they increase the size of the attack surface, precisely when cybersecurity attacks are at an all-time high.
The CoIP SASE Overlay provides application-oriented connectivity; the overlay flips the paradigm, allowing a complex network security problem to instead be treated as an access control problem. This completely avoids the challenge and delays introduced by the need to build infrastructure.
How does the CoIP SASE Overlay work?
A good analogy for the CoIP SASE Overlay is instant messaging. Users can send messages such as text, multimedia, and even files to each other, without building a peer-to-peer connection or having to be on the same network. The CoIP SASE Overlay works much like this, relaying messages from one application to another – it's just that the messages happen to be TCP/IP application traffic. The overlay has been highly optimized for low latency and multi-gigabit flow throughput.
Applications do not need to be modified to use the overlay, and typically aren't even aware of its existence. The overlay is instantiated as a virtual interface, right in the operating system, making authenticated remote endpoints appear to be peers.
User, endpoint, application, and device identity are validated before connections are setup, and continuously verified in accordance with the principles of Zero Trust. Connections are authorized by policy, and can be locked to specific source and destination applications.
What are the benefits of the SASE overlay approach?
The CoIP SASE Overlay effectively decouples security from networking, and associates it instead with the application layer. In other words, the security enforcement is virtually pushed to the application edge. This has several key operational and security benefits:
- It associates security with the application rather than the network, enabling the security policy to follow the workload into any environment for agility
- It serves as a practical model for adopting Zero Trust, reducing the application attack surface for existing applications without a network overhaul
- It avoids the legacy 'infrastructure build' of a unified, shared network, allowing each siloed perimeter (cloud VPC, remote site, etc) to be independently managed and secured.
What problems does a SASE overlay solve?
SASE overlays have been used to address a wide range of complex use cases, including:
- Remote access for employees, vendors, and customers
- Migration of applications from legacy datacenters to public clouds
- Securing OT and critical infrastructure through micro-segmentation in place, and to secure access from cloud



